
| หากต้องการใบเสนอราคา / ใบแจ้งหนี้ ติดต่อได้ทาง LINE Official: @mikroelec |
 |
- จำนวนและราคาสินค้าที่มีอยู่จริงจะตรงกับในเว็บ
- ถ้ากดใส่ตระกร้าได้แสดงว่ามีสินค้าพร้อมส่ง หากจำนวนไม่พอจะมีข้อความแจ้งจำนวนคงเหลือให้ทราบ
- การรับ/ส่งสินค้ามี 3 รูปแบบคือ ส่งพัสดุ / มารับเองที่ร้าน / บริการแอปขนส่งเช่น Grab, LALAMOVE, ฺBolt, อื่นๆ
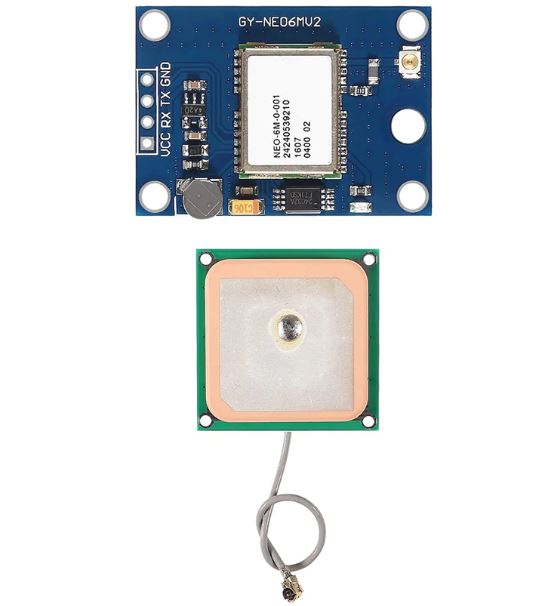
GY-NEO-6MV2 New NEO-6M GPS Module NEO6MV2 With EEPROM MWC APM2.5 Large Antenna For Arduino








| รหัสสินค้า | SKU-02147 |
| หมวดหมู่ | ระบบเครือข่าย GPS / GPRS / GSM |
| ราคา | 190.00 บาท |
| ลงสินค้า | 15 ต.ค. 2565 |
| อัพเดทล่าสุด | 12 ก.พ. 2567 |
- จำนวนและราคาสินค้าที่มีอยู่จริงจะตรงกับในเว็บ
- ถ้ากดใส่ตระกร้าได้แสดงว่ามีสินค้าพร้อมส่ง หากจำนวนไม่พอจะมีข้อความแจ้งจำนวนคงเหลือให้ทราบ
- การรับ/ส่งสินค้ามี 3 รูปแบบคือ ส่งพัสดุ / มารับเองที่ร้าน / บริการแอปขนส่งเช่น Grab, LALAMOVE, ฺBolt, อื่นๆ
รายละเอียดสินค้า
NEO-6M GPS module with the Arduino to get GPS data. GPS stands for Global Positioning System and can be used to determine position, time, and speed if you’re travelling.
Product Description:
GPS Module NEO-6M, 3V-5V Universal
Model: GY-GPS6MV2
Ceramic module edge antenna, super signal
EEPROM Power-Down saves configuration parameter data.
backup battery
LED indicator
Antenna size 25*25 mm
Module size 25mm*35mm
Aperture 3 mm.
Default baud rate: 9600
Compatible with flight control modules
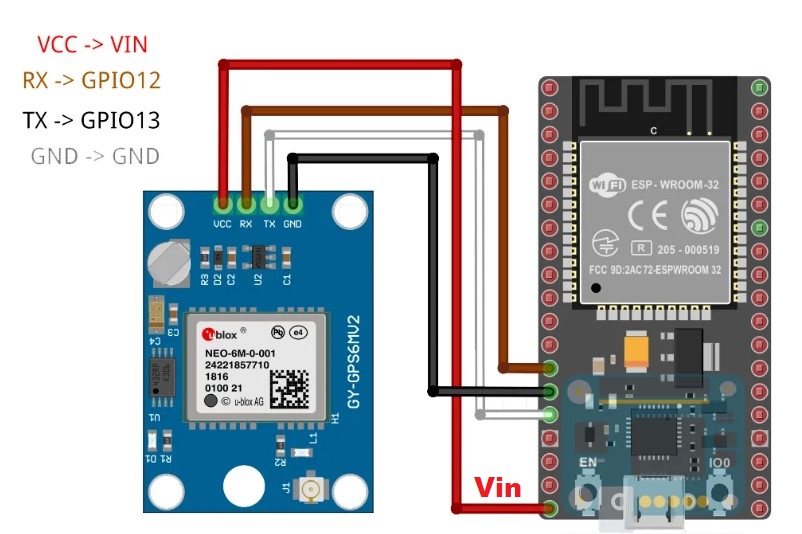
Pin Wiring
The NEO-6M GPS module has four pins: VCC, RX, TX, and GND. The module communicates with the Arduino via serial communication using the TX and RX pins, so the wiring couldn’t be simpler:
| NEO-6M GPS Module | Wiring to Arduino UNO |
| VCC | 5V |
| RX | TX pin defined in the software serial |
| TX | RX pin defined in the software serial |
| GND | GND |
the first position 1-10min. Please be patient and wait for the position.
Schematics
Wire the NEO-6M GPS module to your Arduino by following the schematic below.
Installing the TinyGPS++ Library
Follow the next steps to install the TinyGPS++ library in your Arduino IDE:
- Click here to download the TinyGPSPlus library. You should have a .zip folder in your Downloads folder
- Unzip the .zip folder and you should get TinyGPSPlus-master folder
- Rename your folder from
TinyGPSPlus-masterto TinyGPSPlus - Move the TinyGPSPlus folder to your Arduino IDE installation libraries folder
- Finally, re-open your Arduino IDE
The library provides several examples on how to use it. In your Arduino IDE, you just need to go to File > Examples > TinyGPS++, and choose from the examples provided.
Note: the examples provided in the library assume a baud rate of 4800 for the GPS module. You need to change that to 9600 if you’re using the NEO-6M GPS module.
Getting Location Using the NEO-6M GPS Module and the TinyGPS++ Library
You can get the location in a format that is convenient and useful by using the TinyGPS++ library. Below, we provide a code to get the location from the GPS. This is a simplified version of one of the library examples.
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
static const int RXPin = 4, TXPin = 3;
static const uint32_t GPSBaud = 9600;
// The TinyGPS++ object
TinyGPSPlus gps;
// The serial connection to the GPS device
SoftwareSerial ss(RXPin, TXPin);
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
ss.begin(GPSBaud);
}
void loop(){
// This sketch displays information every time a new sentence is correctly encoded.
while (ss.available() > 0){
gps.encode(ss.read());
if (gps.location.isUpdated()){
Serial.print("Latitude= ");
Serial.print(gps.location.lat(), 6);
Serial.print(" Longitude= ");
Serial.println(gps.location.lng(), 6);
}
}
}
Upload the code to your Arduino, and you should see the location displayed on the serial monitor. After uploading the code, wait a few minutes while the module adjusts the position to get a more accurate data.

Getting More GPS Information Using the TinyGPS++ Library
The TinyGPS++ library allows you to get way more information than just the location, and in a simple way. Besides the location, you can get:
- date
- time
- speed
- course
- altitude
- satellites
- hdop
The code below exemplifies how you can get all that information in a simple way.
/*
* Rui Santos
* Complete Project Details https://randomnerdtutorials.com
*
* Based on the example TinyGPS++ from arduiniana.org
*
*/
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
static const int RXPin = 4, TXPin = 3;
static const uint32_t GPSBaud = 9600;
// The TinyGPS++ object
TinyGPSPlus gps;
// The serial connection to the GPS device
SoftwareSerial ss(RXPin, TXPin);
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
ss.begin(GPSBaud);
}
void loop(){
// This sketch displays information every time a new sentence is correctly encoded.
while (ss.available() > 0){
gps.encode(ss.read());
if (gps.location.isUpdated()){
// Latitude in degrees (double)
Serial.print("Latitude= ");
Serial.print(gps.location.lat(), 6);
// Longitude in degrees (double)
Serial.print(" Longitude= ");
Serial.println(gps.location.lng(), 6);
// Raw latitude in whole degrees
Serial.print("Raw latitude = ");
Serial.print(gps.location.rawLat().negative ? "-" : "+");
Serial.println(gps.location.rawLat().deg);
// ... and billionths (u16/u32)
Serial.println(gps.location.rawLat().billionths);
// Raw longitude in whole degrees
Serial.print("Raw longitude = ");
Serial.print(gps.location.rawLng().negative ? "-" : "+");
Serial.println(gps.location.rawLng().deg);
// ... and billionths (u16/u32)
Serial.println(gps.location.rawLng().billionths);
// Raw date in DDMMYY format (u32)
Serial.print("Raw date DDMMYY = ");
Serial.println(gps.date.value());
// Year (2000+) (u16)
Serial.print("Year = ");
Serial.println(gps.date.year());
// Month (1-12) (u8)
Serial.print("Month = ");
Serial.println(gps.date.month());
// Day (1-31) (u8)
Serial.print("Day = ");
Serial.println(gps.date.day());
// Raw time in HHMMSSCC format (u32)
Serial.print("Raw time in HHMMSSCC = ");
Serial.println(gps.time.value());
// Hour (0-23) (u8)
Serial.print("Hour = ");
Serial.println(gps.time.hour());
// Minute (0-59) (u8)
Serial.print("Minute = ");
Serial.println(gps.time.minute());
// Second (0-59) (u8)
Serial.print("Second = ");
Serial.println(gps.time.second());
// 100ths of a second (0-99) (u8)
Serial.print("Centisecond = ");
Serial.println(gps.time.centisecond());
// Raw speed in 100ths of a knot (i32)
Serial.print("Raw speed in 100ths/knot = ");
Serial.println(gps.speed.value());
// Speed in knots (double)
Serial.print("Speed in knots/h = ");
Serial.println(gps.speed.knots());
// Speed in miles per hour (double)
Serial.print("Speed in miles/h = ");
Serial.println(gps.speed.mph());
// Speed in meters per second (double)
Serial.print("Speed in m/s = ");
Serial.println(gps.speed.mps());
// Speed in kilometers per hour (double)
Serial.print("Speed in km/h = ");
Serial.println(gps.speed.kmph());
// Raw course in 100ths of a degree (i32)
Serial.print("Raw course in degrees = ");
Serial.println(gps.course.value());
// Course in degrees (double)
Serial.print("Course in degrees = ");
Serial.println(gps.course.deg());
// Raw altitude in centimeters (i32)
Serial.print("Raw altitude in centimeters = ");
Serial.println(gps.altitude.value());
// Altitude in meters (double)
Serial.print("Altitude in meters = ");
Serial.println(gps.altitude.meters());
// Altitude in miles (double)
Serial.print("Altitude in miles = ");
Serial.println(gps.altitude.miles());
// Altitude in kilometers (double)
Serial.print("Altitude in kilometers = ");
Serial.println(gps.altitude.kilometers());
// Altitude in feet (double)
Serial.print("Altitude in feet = ");
Serial.println(gps.altitude.feet());
// Number of satellites in use (u32)
Serial.print("Number os satellites in use = ");
Serial.println(gps.satellites.value());
// Horizontal Dim. of Precision (100ths-i32)
Serial.print("HDOP = ");
Serial.println(gps.hdop.value());
}
}
}







วิธีการชำระเงิน
ชำระเงินผ่านธนาคาร
ชำระเงินด้วยการ Scan QR



นโยบายการเปลี่ยนหรือคืนสินค้า
หมายเหตุ
ต้องไม่เสียหายอันเกิดจากใช้งานผิดพลาด ใช้ผิดวิธี ต่อไฟผิดขั้ว จ่ายไฟเกินกำหนด หรืออื่นๆที่ตรวจสอบแล้วไม่ได้เกิดจากความผิดพลาดจากการผลิตสินค้า
Recently viewed
ค้นหาสินค้า/Search
ค้นหาเลขพัสดุ/Track
Categories
Statistic
| หน้าที่เข้าชม | 563,672 ครั้ง |
| ผู้ชมทั้งหมด | 321,315 ครั้ง |
| ร้านค้าอัพเดท | 19 ต.ค. 2568 |
Member
- ระดับ{{userdata.dropship_level_name}}
- ไปหน้าหลักตัวแทน
- ทั้งหมด {{(order_nums && order_nums.all)?'('+order_nums.all+')':''}}
- รอการชำระเงิน {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_payment)?'('+order_nums.wait_payment+')':''}}
- รอตรวจสอบยอดเงิน {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_payment_verify)?'('+order_nums.wait_payment_verify+')':''}}
- รอจัดส่งสินค้า {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_send)?'('+order_nums.wait_send+')':''}}
- รอยืนยันได้รับสินค้า {{(order_nums && (order_nums.wait_receive || order_nums.wait_confirm))?'('+(order_nums.wait_receive+order_nums.wait_confirm)+')':''}}
- รอตรวจสอบข้อร้องเรียน {{(order_nums && order_nums.dispute)?'('+order_nums.dispute+')':''}}
- เรียบร้อยแล้ว {{(order_nums && order_nums.completed)?'('+order_nums.completed+')':''}}
- ทั้งหมด {{(order_nums && order_nums.all)?'('+order_nums.all+')':''}}
- รอการชำระเงิน {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_payment)?'('+order_nums.wait_payment+')':''}}
- รอตรวจสอบยอดเงิน{{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_payment_verify)?'('+order_nums.wait_payment_verify+')':''}}
- รอจัดส่งสินค้า {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_send)?'('+order_nums.wait_send+')':''}}
- ส่งสินค้าเรียบร้อยแล้ว {{(order_nums && order_nums.sent)?'('+order_nums.sent+')':''}}

อีเมล : mikroelec@gmail.com
TOP เลื่อนขึ้นบนสุด




