
| หากต้องการใบเสนอราคา / ใบแจ้งหนี้ ติดต่อได้ทาง LINE Official: @mikroelec |
 |
- จำนวนและราคาสินค้าที่มีอยู่จริงจะตรงกับในเว็บ
- ถ้ากดใส่ตระกร้าได้แสดงว่ามีสินค้าพร้อมส่ง หากจำนวนไม่พอจะมีข้อความแจ้งจำนวนคงเหลือให้ทราบ
- การรับ/ส่งสินค้ามี 3 รูปแบบคือ ส่งพัสดุ / มารับเองที่ร้าน / บริการแอปขนส่งเช่น Grab, LALAMOVE, ฺBolt, อื่นๆ
INA226 โมดูลวัดแรงดันและกระแสไฟฟ้า High Side or Low-Side DC Current Sensor 0-36V 0.01Ohm I2C





| รหัสสินค้า | SKU-01705 |
| หมวดหมู่ | โมดูลวัดแรงดันและกระแสไฟฟ้า |
| ราคา | 85.00 บาท |
| สถานะสินค้า | พร้อมส่ง |
| ลงสินค้า | 7 ก.ย. 2564 |
| อัพเดทล่าสุด | 25 ก.ย. 2567 |
| จำนวน | ชิ้น |
หยิบลงตะกร้า
- จำนวนและราคาสินค้าที่มีอยู่จริงจะตรงกับในเว็บ
- ถ้ากดใส่ตระกร้าได้แสดงว่ามีสินค้าพร้อมส่ง หากจำนวนไม่พอจะมีข้อความแจ้งจำนวนคงเหลือให้ทราบ
- การรับ/ส่งสินค้ามี 3 รูปแบบคือ ส่งพัสดุ / มารับเองที่ร้าน / บริการแอปขนส่งเช่น Grab, LALAMOVE, ฺBolt, อื่นๆ
รายละเอียดสินค้า
| Documentation |
| Datasheet | INA226.pdf |
| Library | INA226 |
| Application Note | - |
nature
The INA226 is a Current Shunt and Power Monitor that supports I2C™-or SMBUS-interfaces. The device monitors both the shunt voltage and the bussupply voltage. The program calibrated the conversion times and average values combined with a volume control multiply enabled to directly read the current, inamperes and in watts.
The INA226 senses current on the common mode bus voltage ranges from 0 V to 36 V, independent of the voltage. The device operates on a single 2.7 V to 5.5 V, typical draw of 330μA of supply current. The device is specified over an operating temperature range between -40°C and125°C and features 16 programmable addresses on an I2C-compatible interface.

feature
Senses bus voltage 0 V to 36 V
• Side or Low-Side Sensing
• Voltage and Power report
• Accuracy:
-0.1% GAIN Error (MAX)
-10 μV Offset (MAX)
• Set an optional average.
• 16 Program Addresses
• Operates from 2.7 V to 5.5 V.
• 10-Pin, DGS (VSSOP) package.
use
• Server
• TELECOM DEVICES
• Computing
• Power Management
• battery
• Power Supplies
• Equipme test
Pin Description
-
VBUS: Voltage bus
-
SDA/SCL: IIC bus, data and clock line
-
Notifications: Multiple alarm output functions
-
A0/A1: IIC Address
-
In +/-: Non-Inverting Analog Input, Inverting Analog Input

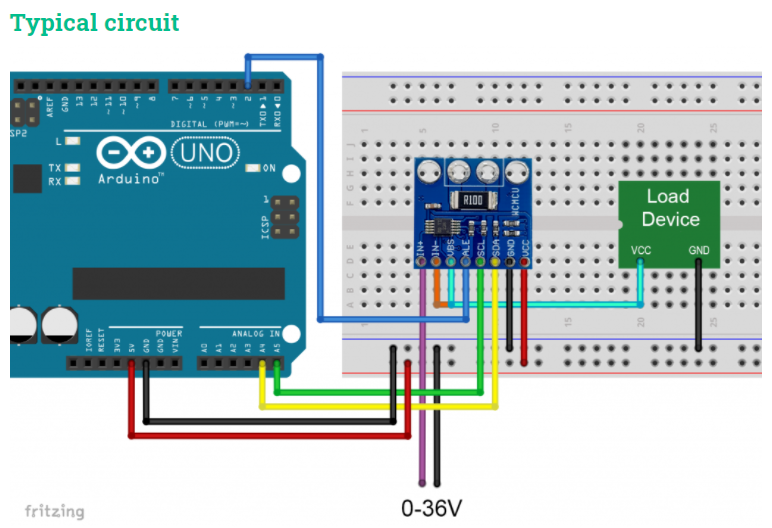
Use of the INA226 library
You can download the library INA226_WE here from GitHub or install it directly with the Library Manager of the Arduino IDE.
#include <Wire.h>
#include <INA226_WE.h>
#define I2C_ADDRESS 0x40
/* There are several ways to create your INA226 object:
* INA226_WE ina226 = INA226_WE() -> uses Wire / I2C Address = 0x40
* INA226_WE ina226 = INA226_WE(ICM20948_ADDR) -> uses Wire / I2C_ADDRESS
* INA226_WE ina226 = INA226_WE(&wire2) -> uses the TwoWire object wire2 / I2C_ADDRESS
* INA226_WE ina226 = INA226_WE(&wire2, I2C_ADDRESS) -> all together
* Successfully tested with two I2C busses on an ESP32
*/
INA226_WE ina226 = INA226_WE(I2C_ADDRESS);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
ina226.init();
/* Set Number of measurements for shunt and bus voltage which shall be averaged
* Mode * * Number of samples *
AVERAGE_1 1 (default)
AVERAGE_4 4
AVERAGE_16 16
AVERAGE_64 64
AVERAGE_128 128
AVERAGE_256 256
AVERAGE_512 512
AVERAGE_1024 1024
*/
//ina226.setAverage(AVERAGE_16); // choose mode and uncomment for change of default
/* Set conversion time in microseconds
One set of shunt and bus voltage conversion will take:
number of samples to be averaged x conversion time x 2
* Mode * * conversion time *
CONV_TIME_140 140 µs
CONV_TIME_204 204 µs
CONV_TIME_332 332 µs
CONV_TIME_588 588 µs
CONV_TIME_1100 1.1 ms (default)
CONV_TIME_2116 2.116 ms
CONV_TIME_4156 4.156 ms
CONV_TIME_8244 8.244 ms
*/
//ina226.setConversionTime(CONV_TIME_1100); //choose conversion time and uncomment for change of default
/* Set measure mode
POWER_DOWN - INA226 switched off
TRIGGERED - measurement on demand
CONTINUOUS - continuous measurements (default)
*/
//ina226.setMeasureMode(CONTINUOUS); // choose mode and uncomment for change of default
/* Set Current Range
* Mode * * Max Current *
MA_400 400 mA
MA_800 800 mA (default)
*/
//ina226.setCurrentRange(MA_800); // choose gain and uncomment for change of default
/* If the current values delivered by the INA226 differ by a constant factor
from values obtained with calibrated equipment you can define a correction factor.
Correction factor = current delivered from calibrated equipment / current delivered by INA226
*/
// ina226.setCorrectionFactor(0.95);
Serial.println("INA226 Current Sensor Example Sketch - Continuous");
ina226.waitUntilConversionCompleted(); //if you comment this line the first data might be zero
}
void loop() {
float shuntVoltage_mV = 0.0;
float loadVoltage_V = 0.0;
float busVoltage_V = 0.0;
float current_mA = 0.0;
float power_mW = 0.0;
ina226.readAndClearFlags();
shuntVoltage_mV = ina226.getShuntVoltage_mV();
busVoltage_V = ina226.getBusVoltage_V();
current_mA = ina226.getCurrent_mA();
power_mW = ina226.getBusPower();
loadVoltage_V = busVoltage_V + (shuntVoltage_mV/1000);
Serial.print("Shunt Voltage [mV]: "); Serial.println(shuntVoltage_mV);
Serial.print("Bus Voltage [V]: "); Serial.println(busVoltage_V);
Serial.print("Load Voltage [V]: "); Serial.println(loadVoltage_V);
Serial.print("Current[mA]: "); Serial.println(current_mA);
Serial.print("Bus Power [mW]: "); Serial.println(power_mW);
if(!ina226.overflow){
Serial.println("Values OK - no overflow");
}
else{
Serial.println("Overflow! Choose higher current range");
}
Serial.println();
delay(3000);
}




วิธีการชำระเงิน
ชำระเงินผ่านธนาคาร
ชำระเงินด้วยการ Scan QR



ไมโครอิเล็กทรอนิกส์
098-xxxxxx-9
Accept All Banks | รับเงินได้จากทุกธนาคาร
นโยบายการเปลี่ยนหรือคืนสินค้า
หากสินค้าชำรุดหรือใช้งานไม่ได้ สามารถขอเปลี่ยนสินค้าได้ภายใน 7 วัน
หมายเหตุ
ต้องไม่เสียหายอันเกิดจากใช้งานผิดพลาด ใช้ผิดวิธี ต่อไฟผิดขั้ว จ่ายไฟเกินกำหนด หรืออื่นๆที่ตรวจสอบแล้วไม่ได้เกิดจากความผิดพลาดจากการผลิตสินค้า
หมายเหตุ
ต้องไม่เสียหายอันเกิดจากใช้งานผิดพลาด ใช้ผิดวิธี ต่อไฟผิดขั้ว จ่ายไฟเกินกำหนด หรืออื่นๆที่ตรวจสอบแล้วไม่ได้เกิดจากความผิดพลาดจากการผลิตสินค้า
Recently viewed
ค้นหาสินค้า/Search
ค้นหาเลขพัสดุ/Track
*ใส่ เบอร์มือถือ หรือ email ที่ใช้ในการสั่งซื้อ
Categories
Statistic
| หน้าที่เข้าชม | 565,255 ครั้ง |
| ผู้ชมทั้งหมด | 322,898 ครั้ง |
| ร้านค้าอัพเดท | 27 ต.ค. 2568 |
Member
คุณเป็นตัวแทนจำหน่าย
- ระดับ{{userdata.dropship_level_name}}
- ไปหน้าหลักตัวแทน
ระดับสมาชิกของคุณ ที่ร้านค้านี้
รายการสั่งซื้อของฉัน
- ทั้งหมด {{(order_nums && order_nums.all)?'('+order_nums.all+')':''}}
- รอการชำระเงิน {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_payment)?'('+order_nums.wait_payment+')':''}}
- รอตรวจสอบยอดเงิน {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_payment_verify)?'('+order_nums.wait_payment_verify+')':''}}
- รอจัดส่งสินค้า {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_send)?'('+order_nums.wait_send+')':''}}
- รอยืนยันได้รับสินค้า {{(order_nums && (order_nums.wait_receive || order_nums.wait_confirm))?'('+(order_nums.wait_receive+order_nums.wait_confirm)+')':''}}
- รอตรวจสอบข้อร้องเรียน {{(order_nums && order_nums.dispute)?'('+order_nums.dispute+')':''}}
- เรียบร้อยแล้ว {{(order_nums && order_nums.completed)?'('+order_nums.completed+')':''}}
- ทั้งหมด {{(order_nums && order_nums.all)?'('+order_nums.all+')':''}}
- รอการชำระเงิน {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_payment)?'('+order_nums.wait_payment+')':''}}
- รอตรวจสอบยอดเงิน{{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_payment_verify)?'('+order_nums.wait_payment_verify+')':''}}
- รอจัดส่งสินค้า {{(order_nums && order_nums.wait_send)?'('+order_nums.wait_send+')':''}}
- ส่งสินค้าเรียบร้อยแล้ว {{(order_nums && order_nums.sent)?'('+order_nums.sent+')':''}}
หน้าแรก | วิธีการสั่งซื้อสินค้า | แจ้งชำระเงิน | บทความ | เว็บบอร์ด | เกี่ยวกับเรา | ติดต่อเรา | ตะกร้าสินค้า | Site Map
ร้านค้าออนไลน์
Inspired by
LnwShop.com (v2)
▲
▼
รายการสั่งซื้อของฉัน
รายการสั่งซื้อของฉัน
ข้อมูลร้านค้านี้

MikroElectronic
จำหน่ายอุปกรณ์อิเล็กทรอนิกส์ โมดูล เครื่องมือ และอุปกรณ์ต่างๆ arduino อาดูโน อะไหล่เครื่องใช้ไฟฟ้า อะไหล่อิเล็กทรอนิกส์ รับออกแบบวงจร เขียนโปรแกรมด้วยอาดูโน รับทำโครงงาน นักเรียนนักศึกษา ให้คำปรึกษาแก้ปัญหาโครงงาน ออกแบบและสร้างงานต้นแบบ ร้านตั้งอยู่ ซอยร่วมสุข ปทุมธานี สถานที่ใกล้เคียง ดอนเมือง สรงประภา ศรีสมาน นนทบุรี แจ้งวัฒนะ
เบอร์โทร : 0984829329
อีเมล : mikroelec@gmail.com
อีเมล : mikroelec@gmail.com
ส่งข้อความติดต่อร้าน
เกี่ยวกับร้านค้านี้
ค้นหาสินค้าในร้านนี้
ค้นหาสินค้า
สินค้าที่ดูล่าสุด
บันทึกเป็นร้านโปรด
Join เป็นสมาชิกร้าน
แชร์หน้านี้
แชร์หน้านี้
↑
TOP เลื่อนขึ้นบนสุด
TOP เลื่อนขึ้นบนสุด
คุณมีสินค้า 0 ชิ้นในตะกร้า สั่งซื้อทันที
สินค้าในตะกร้า ({{total_num}} รายการ)

ขออภัย ขณะนี้ยังไม่มีสินค้าในตะกร้า
ราคาสินค้าทั้งหมด
฿ {{price_format(total_price)}}
- ฿ {{price_format(discount.price)}}
ราคาสินค้าทั้งหมด
{{total_quantity}} ชิ้น
฿ {{price_format(after_product_price)}}
ราคาไม่รวมค่าจัดส่ง
รวมภาษีมูลค่าเพิ่มแล้ว
➜ เลือกซื้อสินค้าเพิ่ม



